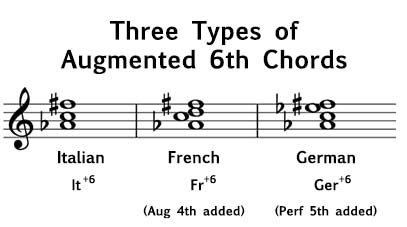
Lesson 32 February 18th, 2022 Lesson 32 Lecture notes: The Neapolitan six is when you take the second degree of a diatonic scale , whether major or minor , lower the root note , and put the said chord in the first inversion . I'll give an example using an F major scale with and without the Neapolitan Six . Without I ( F , A , C ), ii ( G , Bb , D ), iii ( A , C , E ) IV ( Bb , D , F ), V ( C , E , G ), vi ( D , F , A ), viio ( E , G , Bb ), I ( F , A , C ). With I ( F , A , C ), bII6 ( Gb , * Bb , Db ), iii ( A , C , E ) IV ( Bb , D , F ), V ( C , E , G ), vi ( D , F , A ), viio ( E , G , Bb ), I ( F , A , C ). Lowering the root note in the second-degree triad of the diatonic scale turns it from a diminished chord to a majo...